-
Representation Theory
-
Student seminar exercises
Student seminar exercises
- Some exercises from Yuhan
- Determine the dimension of
 , the space of spherical harmonics of degree k on
, the space of spherical harmonics of degree k on  .
.
- Write down some examples of spherical harmonics.
- Explain the decomposition
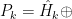
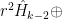
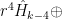
 , or equivalently,
, or equivalently, ![\mathbb{C}[x_1,\ldots,x_n]=\oplus_{k\geq 0}E_k\otimes H_k \mathbb{C}[x_1,\ldots,x_n]=\oplus_{k\geq 0}E_k\otimes H_k](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cmathbb%7BC%7D%5Bx_1%2C%5Cldots%2Cx_n%5D%3D%5Coplus_%7Bk%5Cgeq+0%7DE_k%5Cotimes+H_k&bg=ffffff&fg=000000&s=0) .
.
- Explain why
 is an irreducible representation of
is an irreducible representation of 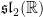 .
.
2022 S2
- Describe the Bruhat decomposition for
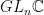 explicitly for small
explicitly for small 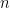 .
.
- Explain why almost all
 have a unique factorisation
have a unique factorisation 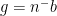 , where
, where 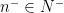 and
and 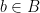 . Here
. Here 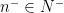 is the subgroup of lower-triangular matrices with 1’s on the diagonal, and
is the subgroup of lower-triangular matrices with 1’s on the diagonal, and 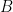 is the subgroup of upper-triangular matrices.
is the subgroup of upper-triangular matrices.
- List a few examples of locally convex, complete, topological vector spaces.
- Explain the completed direct sum in Theorem 6.4.
- Explain why the Heisenberg group
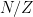 is not a matrix group.
is not a matrix group.
- Explain why the generic fiber of the map
 consists of
consists of 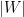 many points in the case of
many points in the case of 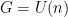 and in general.
and in general.
- Compute the Jacobian of the map
 in the case of
in the case of 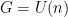 and in general.
and in general.
2022 S1
- What are the groups
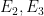 ?
?
- Compute the dimension of
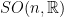 .
.
- What are the Lie algebras of the matrix groups
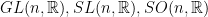 ?
?
- What is
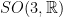 as a manifold?
as a manifold?
- Verify that the map
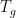 ,
, 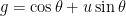 indeed is rotation about the axis
indeed is rotation about the axis  through the angle
through the angle 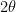 .
.
- Show that the Lie algebras of
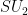 and
and 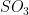 are isomorphic (as Lie algebras).
are isomorphic (as Lie algebras).
- Construct the double coverings
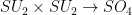 ,
,  and
and 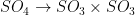 .
.
- Consider the action of
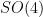 on
on 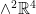 . Find a decomposition of
. Find a decomposition of 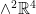 into the direct sum of two stable subspaces.
into the direct sum of two stable subspaces.
- Explain the picture of
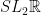 . What is the simply connected covering group of
. What is the simply connected covering group of 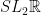 ?
?
- Show that the space of complex structures on
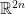 compatible with the inner product is isomorphic to the isotropic Grassmannian of
compatible with the inner product is isomorphic to the isotropic Grassmannian of  .
.
- For the sphere
 , find an isometry
, find an isometry 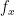 which reverses geodesics through
which reverses geodesics through  . Let
. Let  be the isometry group of
be the isometry group of  . Consider the automorphism
. Consider the automorphism  , where
, where 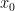 is a fixed point on the sphere. What is the fixed point subgroup
is a fixed point on the sphere. What is the fixed point subgroup 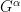 ? What is the stabiliser group
? What is the stabiliser group 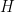 of
of 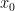 in
in 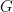 ? What is the relation between
? What is the relation between 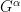 and
and 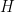 ?
?
- Show that the positive-definite symmetric matrices form an open subset of the vector space of symmetric matrices.
- Prove that an open convex subset in
 is homeomorphic to
is homeomorphic to  .
.
- Describe the polar decomposition of
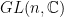 . That is, every invertible complex
. That is, every invertible complex  matrix has a unique factorisation into a positive-definite Hermitian matrix and a unitary matrix (or the other way around).
matrix has a unique factorisation into a positive-definite Hermitian matrix and a unitary matrix (or the other way around).
- Describe the analogous decomposition in Theorem 4.2 for
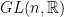 .
.
- Describe the cell decomposition of
 explicitly for small
explicitly for small 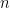 .
.
- Find a maximal torus for the Lie groups
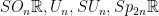 .
.
- Define a smooth structure on
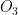 , the projective space
, the projective space 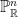 , the Grassmannian
, the Grassmannian  .
.
- Find the tangent space at the identity (Lie algebras) of the Lie groups
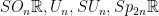 .
.
, the space of spherical harmonics of degree k on
.
, or equivalently,
.
is an irreducible representation of
.
explicitly for small
.
have a unique factorisation
, where
and
. Here
is the subgroup of lower-triangular matrices with 1’s on the diagonal, and
is the subgroup of upper-triangular matrices.
is not a matrix group.
consists of
many points in the case of
and in general.
in the case of
and in general.
?
.
?
as a manifold?
,
indeed is rotation about the axis
through the angle
.
and
are isomorphic (as Lie algebras).
,
and
.
on
. Find a decomposition of
into the direct sum of two stable subspaces.
. What is the simply connected covering group of
?
compatible with the inner product is isomorphic to the isotropic Grassmannian of
.
, find an isometry
which reverses geodesics through
. Let
be the isometry group of
. Consider the automorphism
, where
is a fixed point on the sphere. What is the fixed point subgroup
? What is the stabiliser group
of
in
? What is the relation between
and
?
is homeomorphic to
.
. That is, every invertible complex
matrix has a unique factorisation into a positive-definite Hermitian matrix and a unitary matrix (or the other way around).
.
explicitly for small
.
.
, the projective space
, the Grassmannian
.
.